Quick introduction to Java Programming language - Part 1
Chapters
Variable types in java
Variable is a name of memory location. In Java each variable has a specific type, which determines the size and layout of the variable's memory.
Types of Variable:
There are three types of java variables
- Local variable
- Global/static/class variable
- Instance variable
Local Variables:
- Local variable declared within a method are known as local variable.
- In java local variables must be initialized before using them or else there will be compilation error.
- These variables are not members of class; hence there is no concept of static or non-static here.
- Local variables are available only for a specific method. We cannot use the local variable outside the method.
Example:
public lass RunLocalVar
{
public void setValue()
{
int age =10; //Here "age" is a local variable.
System.out.println("set value method");
}
}
Global Variable:
- Global variable declared within a class directly not within any method are known as Global variable.
- It can be used by any method of the class.
- If we declare a global variables as public static final, then those variables are constants, it should be in upper case.
- Are created when the program starts executed and destroyed when the execution ends.
- Only one copy of global variables in a class, but can any numbers of objects are created from it.
Example:
public class RunGlobalVar
{
int temp; //Here “temp” is a Global variable
float sum=3.2;// Here “sum” is a Global variable
public void setValue()
{
int age =10; //Here “age” is a local variable.
System.out.println(“set value method”);
}
}
Data Members are two types:
Static: Member declared with a keyword “static”.
Non-static: Member declared without static key word (blank).
public class A
{
// data members
Variable 1; // non static
static Variable 2; // static
//Member functions
Method 1;
Method 2;
}
Instance variable:
- These variables are created at the time of object is created by using “new” keyword.
- These variables can be declared in class before or after use.
- Instance variables have default values:
Default values
For numbers the default value is 0
For Booleans it is false and
For object references it is null. - These are declared in a class, but outside a method, constructor.
import java.io.*; public class InstanceVar { public String name; double salary; public void subName(String subjectName){ name = subjectName; } // To assing a value for salary variable. public void setSalary(doubleempSal){ salary = empSal; } // Method to print the employee details. public void printDetails() { System.out.println("Subject name : " + name ); System.out.println("Assigned salary : " + salary); } public static void main(String args[]){ InstanceVar instance = newInstanceVar(); instance.subName("Java Instance Variable"); instance.setSalary(30000); instance.printDetails(); } }
The output: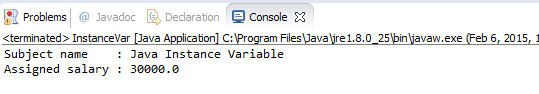
Description
This tutorial is targetted for beginers seeking a quick get on with guide on Java programming language. 3 parts include
- Java basics
- Object oriented programming
- Advance concepts
Each part is subdivided in multiple chapters.
Java basics has the following chapters
- Introduction
- Environment Setup
- Basic Syntax
- Objects and Classes
- Basic Data Types
- Variable Types
- Modifier Types
- Basic Operators
- Loops
- Decision Making
- Numbers Class
- Character and String Class
- Arrays
- Date and Time
- Regular Expression
- Methods
- Streams, Files and I/O
- Exceptions Handling
Thanks for reading and as always, your feedback is very important to us. Let us know how we can improve and if you found any issues with this write up, send us a correction.
Audience
Beginners or students seeking a refresher on Java language
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 9th Mar 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!