Beginners guide to MySQL and MariaDB
Chapters
Using Sequences and getting database Info
MySQL Using Sequence
A sequence is set of integers 1, 2, 3 ... that are generated automatically. Sequences are used in databases since many applications require each row in a table to have a unique value and sequences.
Using AUTO_INCREMENT column:
In MySQL by setting the column as AUTO_INCREMENT a Sequences is created.
CREATE TABLE tmp_book ( id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY (id), name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO tmp_book(id,name) VALUES (NULL,'Learn C#'), (NULL,'Learn Testing');
An example below shows an auto increment column, whose value is auto incremented automatically when a new record is inserted.
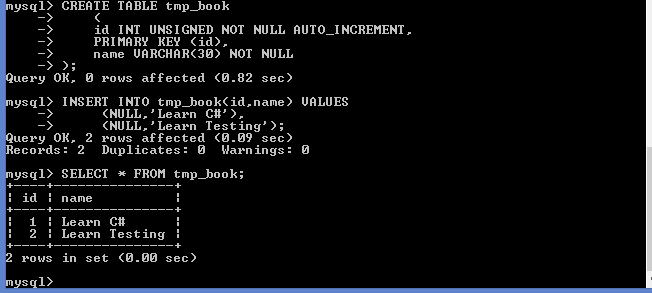
Here are some more insights on AUTO INCREMENTS
Specific value of a Sequence to start with:
MySQL starts an auto increment column from value 1, however while you are creating a new table, you can override that value as shown below
mysql> CREATE TABLE temp ( id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT = 250, PRIMARY KEY (id) );
ID above will start from 250 onwards
You can also use an ALTER statement to alter the auto increment base value as shown below to 250
mysql> ALTER TABLE temp AUTO_INCREMENT = 250;
Database Info
The MySQL provide following information:
- Information about queries result: It includes number of records affected by SELECT, UPDATE or DELETE statement.
- Information about tables and databases: It includes information about the structure of databases and tables.
- Information about MySQL server: It includes current status of database server, version number etc.
Getting Server Metadata:
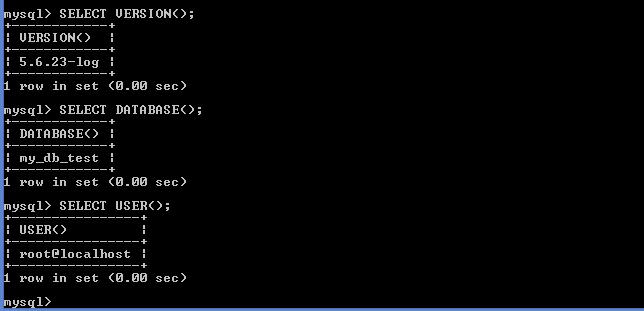
Below are the commands in MySQL which provide various information’s about database server.
|
Command |
Description |
|
SELECT VERSION( ) |
Display Server version string |
|
SELECT DATABASE( ) |
Display Current database name (empty if none) |
|
SELECT USER( ) |
Display Current username |
|
SHOW STATUS |
Display Server status indicators |
|
SHOW VARIABLES |
Display Server configuration variables |
Below are few of the above commands in use.
Description
In this tutorial, we will cover few topics that will give you a heads on start to build your knowledge on. Topics that we will cover briefly but still providing enough information are listed below
- Overview
- Installing on Linux and Windows
- Some useful admin queries for starters
- Connection
- Create Database
- Drop Database
- Select Database
- Data Type
- Create Table
- Drop Table
- Inserting and Selecting data
- Where Clause
- Updating and deleting data
- Like Clause
- Sorting Result
- Using Joins
- Brief introduction to Regex, Transactions and Indexes
- Alter Command
- Temporary Tables
- Database Info
- Using Sequence
- Database Export and Import
- Resetting MySQL/MariaDB Administrator password
Audience
Absolute beginners looking to get a sneak peak into what MySQL. Please remember that this is not a full on guide but a quick introduction to the subject.
Learning Objectives
Get to know MySQL and MariaDB
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 23rd Jun 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!